Embarking on a journey to understand disability insurance beyond its traditional health-related scope, this exploration delves into the diverse types of coverage available, empowering individuals with the knowledge to navigate this complex landscape.
From short-term policies that provide temporary support to long-term plans offering comprehensive protection, this guide unveils the intricacies of each option, ensuring informed decision-making for a secure financial future.
Disability Insurance Beyond Health: Understanding the Concept
Disability insurance goes beyond just protecting your health. It provides financial security in the event that you are unable to work due to an illness or injury. Understanding the different types of disability insurance available and their respective benefits and limitations is crucial for making informed decisions.
Types of Disability Insurance
There are two main types of disability insurance:
- Short-term disability insuranceprovides coverage for a limited period, typically up to 2 years, and replaces a portion of your income if you are unable to work due to a short-term disability.
- Long-term disability insuranceprovides coverage for an extended period, usually for several years or until retirement age, and replaces a portion of your income if you are unable to work due to a long-term disability.
Benefits and Limitations
Each type of disability insurance offers its own set of benefits and limitations:
- Short-term disability insuranceprovides coverage for a shorter period, making it more affordable. However, it may not provide sufficient coverage for those who experience long-term disabilities.
- Long-term disability insuranceprovides coverage for a longer period, ensuring financial security in case of extended disabilities. However, it is generally more expensive and may have stricter eligibility requirements.
Short-Term Disability Insurance
Short-term disability insurance provides financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to a temporary disability. Unlike long-term disability insurance, which covers disabilities that last for an extended period, short-term disability insurance typically covers disabilities that last for a few weeks or months.
Qualifying conditions for short-term disability insurance vary depending on the policy, but common examples include:
- Illness or injury
- Pregnancy or childbirth
- Surgery or medical procedures
Benefit periods for short-term disability insurance also vary depending on the policy, but they typically range from a few weeks to six months.
Coverage and Eligibility
Short-term disability insurance typically covers a portion of an individual’s income, usually between 60% and 80%. Eligibility for short-term disability insurance is generally based on the following criteria:
- Employment status: Individuals must be employed by a company that offers short-term disability insurance.
- Waiting period: There is often a waiting period before benefits can be received, typically ranging from one to seven days.
- Disability definition: The policy must define what constitutes a disability that is covered under the plan.
It’s important to note that short-term disability insurance does not cover all types of disabilities. For example, it may not cover disabilities that are caused by pre-existing conditions or disabilities that are considered permanent.
Long-Term Disability Insurance
Long-term disability insurance provides financial protection in the event of a disability that prevents you from working for an extended period, typically more than 90 days. It offers a safety net to help cover expenses and maintain your standard of living if you become unable to earn an income due to a long-term illness or injury.
Coverage and Benefits
Long-term disability insurance typically covers a wide range of disabilities, including:
- Physical disabilities (e.g., paralysis, amputation, chronic pain)
- Mental health disabilities (e.g., depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder)
- Cognitive disabilities (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, dementia)
Benefits under long-term disability insurance vary depending on the policy, but they typically include:
- Monthly income replacement (typically 60-80% of your pre-disability income)
- Cost-of-living adjustments to keep pace with inflation
- Rehabilitation and vocational training benefits
Eligibility and Benefit Periods
Eligibility for long-term disability insurance is based on your occupation and income. Typically, you must be employed and earning a certain amount of money to qualify for coverage.Benefit periods for long-term disability insurance can vary, but they typically range from two to five years, or until you reach retirement age.
Some policies may offer lifetime benefits for certain disabilities.
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)

Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a federal assistance program that provides financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. To be eligible for SSDI, you must meet the following requirements:
- You must have worked long enough and recently enough to qualify for Social Security disability benefits.
- You must have a disability that is expected to last for at least 12 months or result in death.
- Your disability must prevent you from doing any substantial gainful activity.
The application process for SSDI can be complex and time-consuming. It is important to gather all of the necessary documentation and to have a clear understanding of the eligibility requirements. The Social Security Administration (SSA) will review your application and make a determination on your eligibility.
If you are approved for benefits, you will receive monthly payments from the SSA.SSDI benefits can provide a vital source of income for individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. These benefits can help to cover the costs of medical care, housing, food, and other essential expenses.
Applying for SSDI
The application process for SSDI can be complex and time-consuming. It is important to gather all of the necessary documentation and to have a clear understanding of the eligibility requirements. The SSA will review your application and make a determination on your eligibility.
If you are approved for benefits, you will receive monthly payments from the SSA.
Benefits of SSDI
SSDI benefits can provide a vital source of income for individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. These benefits can help to cover the costs of medical care, housing, food, and other essential expenses.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance

Workers’ compensation insurance is a form of insurance that provides financial protection to employees who suffer injuries or illnesses arising from their work. It covers medical expenses, lost wages, and other related costs associated with the injury or illness.Examples of covered injuries and illnesses include:
- Physical injuries, such as fractures, sprains, and cuts
- Occupational diseases, such as carpal tunnel syndrome and asbestosis
- Mental health conditions, such as stress and anxiety caused by work-related factors
Private Disability Insurance

Private disability insurance offers a customizable safety net, providing financial protection in the event of a disabling injury or illness. Unlike government programs, private insurance allows you to tailor coverage to your specific needs and circumstances.
Benefits of Private Disability Insurance:
- Flexibility:Choose coverage amounts, benefit periods, and waiting periods that suit your financial situation.
- Comprehensive coverage:Protect against a wide range of disabilities, including physical, mental, and occupational impairments.
- Guaranteed income:Receive regular payments to cover expenses and maintain your standard of living during disability.
- Tax-free benefits:In most cases, disability insurance benefits are tax-free, reducing the financial burden of disability.
Policy Options and Riders
Private disability insurance policies offer various options and riders to enhance coverage:
- Own-occupation vs. Any-occupation definition of disability:The own-occupation definition pays benefits if you cannot perform your current job, while the any-occupation definition pays if you cannot perform any gainful work.
- Guaranteed insurability riders:Allow you to increase coverage amounts in the future without medical underwriting.
- Cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs):Help benefits keep pace with inflation over time.
- Partial disability benefits:Provide a reduced benefit if you can only work part-time due to disability.
Group Disability Insurance
Group disability insurance is a type of disability insurance that is offered through an employer. It provides income protection for employees who are unable to work due to a disability.Employers may offer group disability insurance as a voluntary benefit or as a mandatory part of their employee benefits package.
The coverage provided by group disability insurance typically includes short-term disability insurance and long-term disability insurance.
Employer’s Role
Employers play a key role in providing group disability insurance to their employees. They are responsible for selecting the insurance provider, determining the coverage levels, and paying the premiums. Employers may also offer additional benefits, such as coverage for pre-existing conditions or coverage for employees who are not able to work due to a non-disabling injury or illness.
Disability Income Insurance
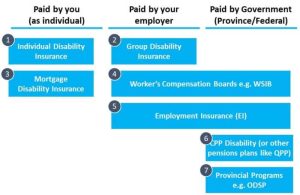
Disability income insurance provides a safety net by replacing a portion of your income if you become disabled and unable to work. It differs from other types of disability insurance by focusing on income replacement rather than covering medical expenses or providing long-term care.
When you purchase disability income insurance, you choose a monthly benefit amount that you would receive if you become disabled. The benefit amount is typically a percentage of your pre-disability income, such as 60% or 70%. The policy also specifies a waiting period, which is the amount of time you must be disabled before you start receiving benefits.
Factors Affecting Benefit Amounts
Several factors can affect the benefit amount you receive from disability income insurance, including:
- Your income:The higher your income, the higher your benefit amount will be.
- Your age:Younger workers typically pay lower premiums but receive lower benefit amounts than older workers.
- Your occupation:Workers in high-risk occupations, such as construction workers or firefighters, typically pay higher premiums but receive higher benefit amounts.
- Your health:If you have a pre-existing medical condition, you may pay higher premiums or be denied coverage altogether.
Disability Insurance for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals face unique challenges in securing disability coverage. They lack the employer-sponsored plans often available to traditional employees, making it essential for them to explore alternative options to protect their income in the event of an unexpected disability.
Strategies for Obtaining Disability Coverage
Self-employed individuals have several strategies to obtain disability coverage:
- Individual Disability Insurance:This policy provides coverage for lost income due to a disability, regardless of the cause. Premiums are typically higher than employer-sponsored plans, but it offers flexibility and customization.
- Group Disability Insurance:Some professional organizations and associations offer group disability insurance plans to their members. These plans often have lower premiums and simplified underwriting processes.
- High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs):HDHPs have higher deductibles than traditional health insurance plans, but they come with HSAs. HSAs allow individuals to save pre-tax dollars for qualified medical expenses, including disability-related costs.
- Long-Term Care Insurance:This type of insurance provides coverage for long-term care expenses, including those related to disabilities. It can supplement disability insurance by covering costs not covered by traditional disability policies.
Disability Insurance for Specific Occupations
Certain occupations pose higher risks of disability due to the nature of the work or the environment. These include jobs involving physical labor, hazardous conditions, or repetitive motions.
For individuals in such occupations, specialized disability insurance options are available to provide tailored coverage that meets their unique needs.
Specialized Disability Insurance Options
- Occupation-Specific Disability Insurance:Designed for specific professions, these policies consider the unique risks and potential disabilities associated with the occupation.
- High-Risk Disability Insurance:Provides coverage for individuals in occupations with inherently high risks, such as construction workers, firefighters, and police officers.
- Residual Disability Insurance:Supplements existing disability coverage by providing benefits if an individual can only perform some, but not all, of their job duties due to a disability.
Comparing Disability Insurance Policies
When comparing disability insurance policies, it’s essential to consider various factors that impact coverage, cost, and accessibility.
To help you make an informed decision, we’ve organized a table comparing different disability insurance policies based on key considerations:
Coverage
- Definition of Disability:Determine the specific conditions or limitations that qualify as a disability.
- Benefit Amount:The maximum monthly benefit you can receive if disabled.
- Benefit Period:The length of time you can receive benefits, typically ranging from a few months to several years.
- Waiting Period:The period you must be disabled before benefits start, typically ranging from a few weeks to a year.
Premiums
- Premium Amount:The monthly or annual cost of the policy.
- Premium Structure:Flat-rate or graded premiums, where the premium increases over time.
- Discounts:Potential discounts for factors such as good health, occupation, or multiple policies.
Other Considerations
- Renewability:Whether the policy can be renewed after the initial term.
- Portability:The ability to transfer coverage to a new employer or insurer.
- Customer Service:The availability and responsiveness of the insurance company’s customer support.
Last Recap
In closing, disability insurance extends far beyond its health implications, offering a lifeline for individuals facing unexpected life events that impair their ability to earn an income. By exploring the various types of coverage, individuals can tailor a plan that aligns with their unique circumstances, providing peace of mind and financial stability during challenging times.

