In the dynamic realm of modern insurance markets, embedded insurance has emerged as a transformative force, seamlessly integrating protection into everyday products and services. This comprehensive overview will delve into the intricacies of embedded insurance, exploring its multifaceted benefits, diverse applications, and the challenges that shape its implementation.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey into the world of embedded insurance, where innovation and accessibility converge to redefine the insurance landscape.
Embedded insurance offers a myriad of advantages for consumers, businesses, and insurers alike. Consumers enjoy the convenience of accessing insurance coverage effortlessly, tailored to their specific needs. Businesses leverage embedded insurance to enhance customer loyalty, differentiate their offerings, and generate additional revenue streams.
Insurers, in turn, gain access to new markets and distribution channels, expanding their reach and driving growth.
Embedded Insurance Definition

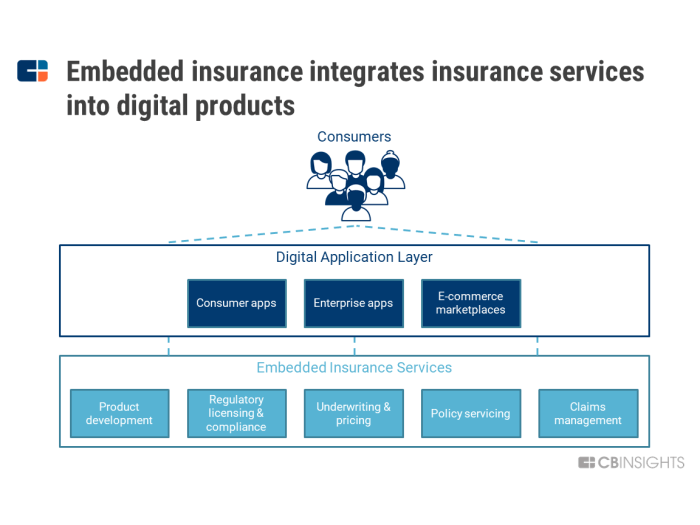
Embedded insurance refers to the integration of insurance products and services into non-insurance products and services. This concept has gained significant traction in modern insurance markets, offering innovative ways to distribute and access insurance coverage.
Embedded insurance is characterized by its seamless integration into customer touchpoints, providing convenient and tailored insurance solutions. It enables businesses to enhance their product offerings, improve customer experience, and generate additional revenue streams. For consumers, embedded insurance offers simplified access to insurance coverage, often at a lower cost and with minimal effort.
Key Characteristics of Embedded Insurance
- Integrated into Non-Insurance Products:Embedded insurance is seamlessly integrated into non-insurance products or services, such as ride-sharing, e-commerce, or subscription services.
- Tailored to Specific Needs:Embedded insurance products are designed to meet the specific needs and risks associated with the underlying non-insurance product or service.
- Convenient and Accessible:Embedded insurance offers convenient access to insurance coverage through familiar channels, such as mobile apps or online platforms.
- Automated and Frictionless:The underwriting and claims processes are often automated, providing a frictionless and efficient experience for customers.
Benefits of Embedded Insurance
- Enhanced Customer Experience:Embedded insurance improves customer experience by providing tailored and convenient insurance solutions.
- Increased Revenue Streams:Businesses can generate additional revenue streams by offering embedded insurance products and services.
- Reduced Distribution Costs:Embedded insurance eliminates the need for traditional distribution channels, resulting in reduced distribution costs.
- Improved Risk Management:Embedded insurance can help businesses manage their risks associated with their products or services.
Types of Embedded Insurance

Embedded insurance encompasses a wide array of insurance products seamlessly integrated into non-insurance transactions. Each type is meticulously designed to cater to specific industries and customer requirements.
The versatility of embedded insurance extends to various sectors, including retail, healthcare, travel, and financial services. By tailoring insurance solutions to specific industries, providers can effectively address unique risks and customer needs.
Retail
- Purchase protection: Protects against loss, damage, or theft of purchased items.
- Extended warranty: Extends the manufacturer’s warranty, providing additional coverage for repairs or replacements.
- Return protection: Reimburses customers for returned items, eliminating the risk of financial loss.
Healthcare
- Telehealth coverage: Provides access to virtual doctor consultations, reducing healthcare costs and improving convenience.
- Prescription drug coverage: Covers the cost of prescription medications, making healthcare more affordable.
- Dental and vision insurance: Offers coverage for dental and vision care, complementing traditional health insurance.
Travel
- Travel insurance: Protects against trip cancellations, lost luggage, medical emergencies, and other travel-related risks.
- Flight delay insurance: Reimburses passengers for expenses incurred due to flight delays or cancellations.
- Rental car insurance: Provides coverage for damage or theft of rental vehicles.
Financial Services
- Loan protection insurance: Covers loan repayments in the event of job loss, disability, or death.
- Credit card protection insurance: Protects against unauthorized purchases or fraud on credit cards.
- Identity theft insurance: Reimburses victims of identity theft for expenses incurred in restoring their identity.
Distribution Channels for Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance is distributed through various channels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The choice of distribution channel depends on factors such as the target market, the type of insurance product, and the regulatory environment.
Direct-to-Consumer
- Insurance companies sell embedded insurance directly to consumers through their own websites or mobile apps.
- This channel allows insurers to control the customer experience and build direct relationships with policyholders.
- However, it can be challenging to reach a large audience without significant marketing investment.
Partnerships with Non-Insurance Companies
- Insurance companies partner with non-insurance companies to offer embedded insurance as part of their products or services.
- This channel allows insurers to reach a wider audience and leverage the distribution network of their partners.
- However, it can be challenging to align incentives and ensure that the embedded insurance product is a good fit for the partner’s customer base.
Embedded Insurance Marketplaces
- Embedded insurance marketplaces are platforms that connect insurance companies with non-insurance companies.
- This channel allows insurers to access a wider range of distribution partners and simplifies the process of integrating embedded insurance into non-insurance products and services.
- However, it can be challenging to stand out from the competition and differentiate one’s products in a crowded marketplace.
Examples of successful partnerships in embedded insurance include:
- Amazon’s partnership with AIG to offer embedded insurance on its e-commerce platform.
- Uber’s partnership with Metromile to offer usage-based insurance to its drivers.
- Google’s partnership with Lemonade to offer embedded renters insurance through its Nest smart home devices.
Benefits of Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance offers numerous advantages for consumers, businesses, and insurers alike. It enhances customer experience, drives business growth, and streamlines insurance processes.
For consumers, embedded insurance provides convenience and accessibility. It eliminates the need for separate insurance policies and simplifies the insurance purchasing process. By integrating insurance into non-insurance products or services, consumers can easily protect themselves against specific risks without going through complex insurance procedures.
Benefits for Businesses
- Increased customer engagement:Embedded insurance can enhance customer loyalty and engagement by offering additional value and protection.
- New revenue streams:Businesses can generate additional revenue by partnering with insurers and offering embedded insurance as part of their product or service.
- Improved customer experience:By providing seamless and convenient insurance solutions, businesses can improve the overall customer experience and build stronger relationships.
Benefits for Insurers
- Expanded distribution channels:Embedded insurance allows insurers to reach new customer segments and expand their distribution channels.
- Enhanced risk assessment:By integrating with non-insurance data sources, insurers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of customer risk profiles.
- Reduced operating costs:Automating insurance processes through embedded insurance can reduce administrative costs and improve operational efficiency.
In conclusion, embedded insurance offers a wide range of benefits for consumers, businesses, and insurers. It enhances customer experience, drives business growth, and streamlines insurance processes. By leveraging the power of technology and collaboration, embedded insurance is transforming the insurance industry and making protection more accessible and convenient for all.
Challenges of Embedded Insurance

Implementing and managing embedded insurance programs can pose several challenges for businesses. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful implementation and long-term success.
Potential risks and obstacles include:
Regulatory and Compliance
- Navigating complex insurance regulations and compliance requirements.
- Ensuring compliance with data privacy and consumer protection laws.
- Addressing potential conflicts of interest and ensuring transparency.
Integration and Technology
- Integrating embedded insurance seamlessly into existing platforms and processes.
- Managing data exchange and ensuring secure and efficient communication between partners.
- Addressing potential technological complexities and compatibility issues.
Customer Experience
- Ensuring a seamless and intuitive customer experience throughout the insurance process.
- Providing clear and concise information about insurance coverage and terms.
- Addressing potential customer concerns and managing expectations.
Pricing and Risk Assessment
- Determining appropriate pricing models for embedded insurance products.
- Accurately assessing risks and underwriting policies in a non-traditional context.
- Managing potential adverse selection and moral hazard issues.
Partnership Management
- Building and maintaining strong partnerships with insurance carriers and other stakeholders.
- Managing expectations, aligning incentives, and ensuring effective collaboration.
- Addressing potential conflicts of interest and managing reputational risks.
Future of Embedded Insurance
Embedded insurance is poised for significant growth and evolution in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behavior. Emerging trends, such as the increasing adoption of digital platforms and the rise of insurtech startups, will shape the future of embedded insurance.
Emerging Trends
- Digitalization and Automation:The integration of embedded insurance into digital platforms and processes will streamline insurance distribution and reduce costs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML algorithms will enhance risk assessment, underwriting, and claims processing, leading to personalized and efficient insurance solutions.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Wearables:IoT devices and wearables will provide real-time data on user behavior and risk exposure, enabling tailored insurance products and services.
- Open Insurance and Partnerships:Collaboration between insurers, technology providers, and non-insurance companies will foster innovation and expand distribution channels for embedded insurance.
Conclusion
As the future of embedded insurance unfolds, its potential for growth and evolution is boundless. Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, will continue to reshape the industry, enabling even more seamless and personalized insurance experiences. Embedded insurance is poised to become an integral part of our daily lives, providing peace of mind and financial protection wherever we go.
Embrace the transformative power of embedded insurance and unlock a world of possibilities.
