Navigating the complexities of health insurance can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding deductibles. Demystifying Deductibles: How Much Should You Really Pay Out-of-Pocket? aims to shed light on this often-confusing topic, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of deductibles, exploring their types, factors to consider when choosing one, and strategies for managing them effectively. By the end of this discussion, you’ll have a clear understanding of how deductibles work and how to optimize your healthcare spending.
Defining Deductibles
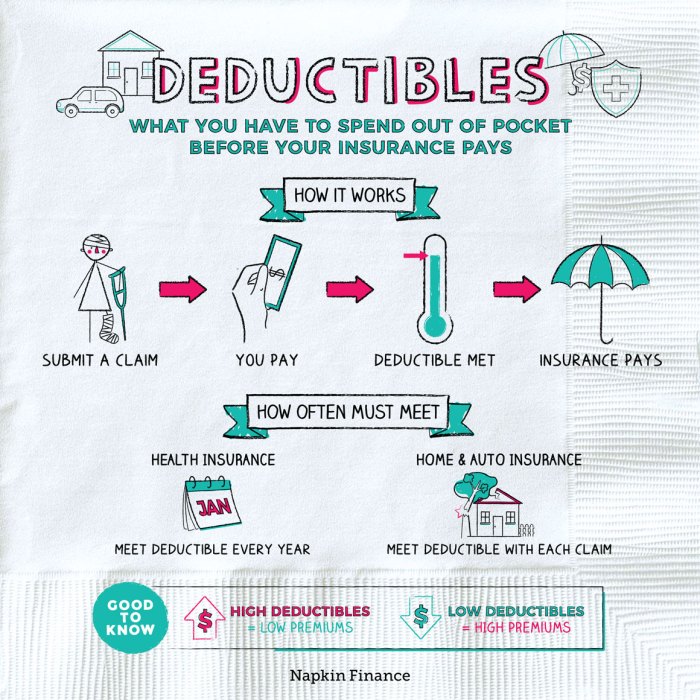
Deductibles are an essential component of many insurance policies. They represent the amount of money you, as the policyholder, are responsible for paying out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Deductibles can vary significantly depending on the type of insurance policy you have and the coverage you choose.
It’s important to understand how deductibles work to make informed decisions about your insurance coverage. By carefully considering your deductible options, you can optimize your financial protection and avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
Distinguishing Deductibles from Premiums and Co-pays
Deductibles are distinct from premiums and co-pays, which are other common insurance terms.
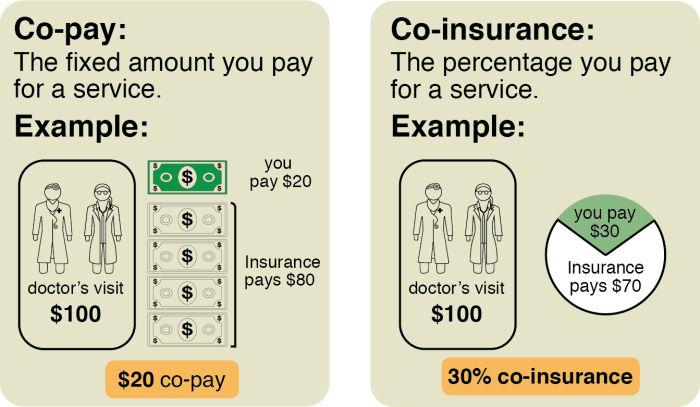
- Premiumsare the regular payments you make to your insurance company to maintain your coverage. Premiums are typically paid monthly or annually.
- Co-paysare fixed amounts you pay for specific medical services, such as doctor’s visits or prescription drugs. Co-pays are typically paid at the time of service.
Types of Deductibles

Deductibles vary in their structure and how they are applied. Understanding the different types of deductibles can help you choose the plan that best suits your needs and budget.
Annual Deductible
An annual deductible is a fixed amount that you must pay out-of-pocket for covered healthcare services before your insurance begins to cover costs. This type of deductible resets each calendar year.
- Example:If you have a $500 annual deductible, you will be responsible for paying the first $500 of eligible healthcare expenses before your insurance starts to cover the costs.
Per-Visit Deductible
A per-visit deductible is a set amount that you must pay for each doctor’s visit, regardless of the type of service received. This type of deductible does not reset over time.
- Example:If you have a $20 per-visit deductible, you will pay $20 for each doctor’s visit, even if you see the same doctor multiple times for the same condition.
Flat-Rate Deductible
A flat-rate deductible is a one-time payment that you make for a specific service or procedure. This type of deductible is not tied to a specific time period and is typically used for elective procedures, such as cosmetic surgery or dental work.
- Example:If you have a $500 flat-rate deductible for cosmetic surgery, you will pay $500 upfront before the procedure is performed.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Deductible
Selecting an appropriate deductible involves weighing various factors that influence your healthcare needs and financial situation. Understanding these considerations will help you make an informed decision.
Health Needs
- Consider your overall health status and the likelihood of needing medical services.
- If you anticipate frequent doctor visits, medications, or potential surgeries, a lower deductible may be more suitable.
- If you are generally healthy and expect minimal healthcare expenses, a higher deductible could be more cost-effective.
Financial Situation
- Evaluate your monthly budget and determine how much you can comfortably allocate towards healthcare expenses.
- Consider your savings and emergency fund to ensure you can cover high out-of-pocket costs associated with a low deductible.
- If your financial resources are limited, a higher deductible may be a viable option, provided you can manage the potential risks.
Risk Tolerance
- Assess your willingness to assume financial risk in the event of unexpected medical expenses.
- If you prefer a lower risk profile, a lower deductible may be preferred, as it limits your potential out-of-pocket expenses.
- If you are comfortable with a higher level of risk, a higher deductible can lead to lower monthly premiums.
Balancing these factors will help you determine the optimal deductible for your individual circumstances. Consider consulting with a healthcare professional or financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Calculating Out-of-Pocket Costs
Determining your out-of-pocket costs is crucial for budgeting and planning your healthcare expenses. These costs are based on your deductible and other insurance coverage.
To calculate your out-of-pocket costs, follow these steps:
- Identify your deductible: This is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in.
- Calculate your copayments and coinsurance: Copayments are fixed amounts you pay for specific medical services, while coinsurance is a percentage of the cost you pay after meeting your deductible.
- Estimate your potential medical expenses: Consider upcoming appointments, medications, or procedures you may need and estimate their costs.
- Add up your expenses: Combine your deductible, copayments, coinsurance, and any other potential medical expenses.
Example Calculation
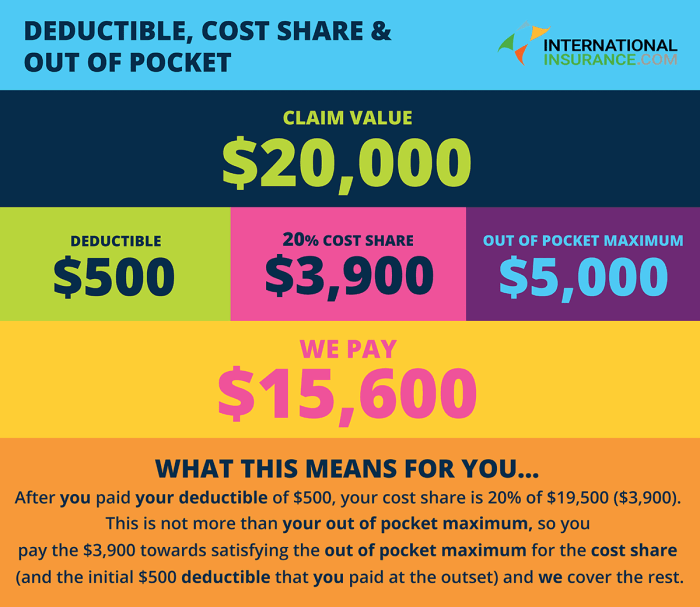
Let’s say you have a $1,000 deductible, a $20 copayment for doctor’s visits, and a 20% coinsurance for hospital stays.
- If you visit the doctor twice, your copayment would be $40.
- If you have a hospital stay that costs $5,000, your coinsurance would be $1,000 (20% of $5,000).
In this scenario, your total out-of-pocket costs would be $1,040 ($1,000 deductible + $40 copayments + $1,000 coinsurance).
Strategies for Managing Deductibles
Managing deductibles effectively can help reduce out-of-pocket healthcare expenses. Here are some strategies to consider:
Budgeting
Create a budget that allocates funds specifically for healthcare expenses, including deductibles. This ensures you have the necessary funds available when needed.
Negotiating with Providers
In some cases, you may be able to negotiate a lower deductible with your healthcare provider. This can be especially beneficial if you have a high deductible health plan (HDHP).
Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
FSAs are tax-advantaged accounts that allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for qualified medical expenses, including deductibles. This can reduce your overall healthcare costs.
Pros and Cons
- Budgeting:Pros – Ensures you have funds available for deductibles; Cons – Requires discipline and planning.
- Negotiating:Pros – Can potentially lower deductibles; Cons – May not be successful in all cases.
- FSAs:Pros – Tax savings; Cons – Funds must be used within the plan year or they are forfeited.
Impact of Deductibles on Healthcare Utilization
Deductibles have a significant impact on healthcare utilization. They can discourage individuals from seeking necessary medical care, leading to potential health risks and increased costs in the long run. Conversely, deductibles can promote cost-consciousness and encourage preventive care.
Research suggests that higher deductibles are associated with lower rates of healthcare utilization, particularly for non-urgent and preventive care. A study by the Commonwealth Fund found that individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) were less likely to have regular checkups, mammograms, and colonoscopies compared to those with low-deductible plans.
Positive Impact
Despite the potential drawbacks, deductibles can also have positive effects on healthcare utilization. By requiring individuals to pay a portion of their medical expenses, deductibles can promote cost-consciousness and encourage preventive care.
- Cost-consciousness:Deductibles can make individuals more aware of the cost of healthcare services, leading them to make more informed decisions about their healthcare spending.
- Preventive care:By encouraging individuals to meet their deductible early in the year, deductibles can promote preventive care, such as regular checkups and screenings, which can help identify and address health issues before they become more serious and costly.
Deductibles in Different Insurance Plans
Deductibles vary across different types of insurance plans, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs typically have lower deductibles than other plans, but they also have more restrictions on which providers you can see and what services are covered.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs have higher deductibles than HMOs, but they offer more flexibility in choosing providers and services. You can see any provider you want, but you’ll pay more for out-of-network care.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs have the highest deductibles, but they also come with lower monthly premiums. HDHPs are often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA), which allows you to save money for healthcare expenses on a pre-tax basis.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance and Deductibles
Employer-sponsored health insurance plans often play a significant role in determining the deductibles that employees face. Employers have the authority to set deductibles for these plans, which can vary widely depending on factors such as the size of the company, industry, and overall healthcare costs.
Employer contributions to health insurance premiums can significantly impact the affordability of deductibles for employees. Employers may choose to contribute a fixed amount or a percentage of the premium, which can reduce the out-of-pocket costs for employees with higher deductibles.
Employer Contributions and Deductible Affordability
When employers make substantial contributions to health insurance premiums, employees may be able to afford higher deductibles without experiencing significant financial hardship. This is because the employer’s contribution effectively lowers the employee’s monthly premium payments, leaving more room in their budget for out-of-pocket expenses.
Conversely, employers who make smaller contributions or none at all may force employees to choose lower deductibles to keep their monthly premiums manageable. This can limit the employee’s ability to save money on healthcare costs in the long run.
Government Regulations and Deductibles
Government regulations play a significant role in shaping deductible levels and consumer choices in healthcare insurance. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced several provisions that impact deductibles, including:
Annual Deductible Limits
The ACA sets annual deductible limits for health insurance plans sold on the individual and small group markets. For 2023, the maximum annual deductible for these plans is $8,700 for self-only coverage and $17,400 for family coverage.
Essential Health Benefits
The ACA requires health insurance plans to cover a set of essential health benefits (EHBs), which include preventive care, maternity care, and prescription drugs. Deductibles cannot apply to preventive care services, such as annual physicals and vaccinations.
Impact on Consumer Choices
Government regulations impact consumer choices by limiting the maximum deductible levels and ensuring that certain essential health services are covered without deductibles. This helps to protect consumers from high out-of-pocket costs and ensures access to necessary healthcare services.
Deductibles and Healthcare Costs
Deductibles play a crucial role in shaping overall healthcare costs. Higher deductibles can lead to lower insurance premiums, but they also increase the amount of money individuals must pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in.
The impact of deductibles on healthcare spending is complex and varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s health status, the type of healthcare services they utilize, and the availability of other forms of financial assistance.
Impact on Healthcare Utilization
High deductibles may discourage individuals from seeking necessary healthcare services, leading to delayed or neglected care. This can have long-term consequences for their health and well-being, potentially leading to more severe and costly health conditions in the future.
Impact on Affordability
For individuals with limited financial resources, high deductibles can pose a significant barrier to accessing affordable healthcare. They may be forced to delay or forego necessary care, which can have detrimental effects on their health and financial stability.
Wrap-Up
Understanding deductibles is crucial for maximizing the value of your health insurance. By carefully considering your health needs, financial situation, and risk tolerance, you can choose a deductible that aligns with your circumstances. Remember, the goal is to strike a balance between affordability and coverage, ensuring you have access to the healthcare you need without breaking the bank.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, deductibles will likely remain an integral part of health insurance plans. By staying informed and adopting proactive strategies, you can navigate the complexities of deductibles and make informed choices that support your overall health and well-being.
