Navigating the complexities of renters insurance versus homeowners insurance can be a daunting task. However, understanding the intricacies of each option empowers individuals to make informed decisions that safeguard their dwellings and personal belongings. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of both insurance types, providing a roadmap to selecting the coverage that aligns with your unique needs and circumstances.
As you embark on this journey, consider the factors that shape your lifestyle, financial situation, and property ownership goals. By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each insurance type, you can ensure that your dwelling is adequately protected against unforeseen events.
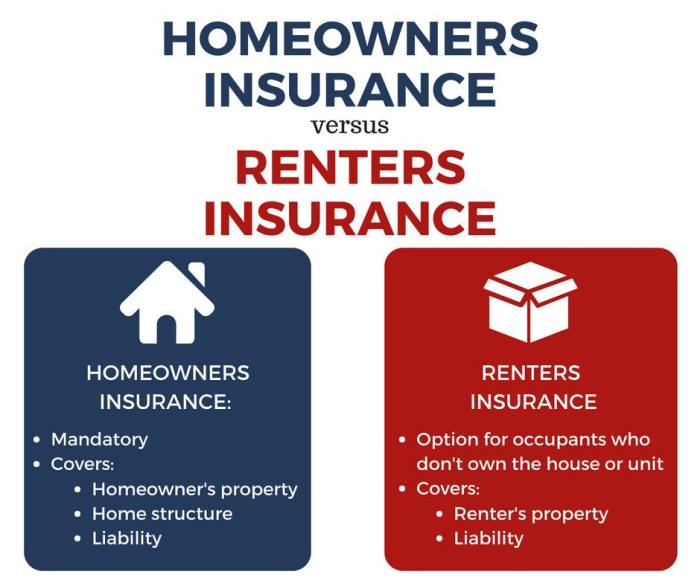
Types of Insurance
Insurance is a contract between you and an insurance company, where you pay a premium in exchange for financial protection against specific risks. There are various types of insurance relevant to renters and homeowners, each providing different coverage options.
Renters Insurance
Renters insurance protects your personal belongings, such as furniture, clothing, and electronics, in case of theft, damage, or loss. It also provides liability coverage in case someone is injured or their property is damaged while visiting your rented space.
Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is more comprehensive than renters insurance, as it covers both the structure of your home and your personal belongings. It typically includes coverage for damage caused by fire, theft, vandalism, and weather events. Additionally, it provides liability coverage and may include additional options such as coverage for detached structures, personal property off-premises, and loss of use.
Coverage Differences
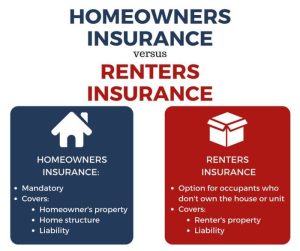
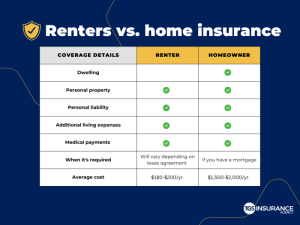
Renters and homeowners insurance policies provide different levels of coverage for the dwelling, personal property, and liability.
Dwelling Coverage
Renters insurance only covers the personal property of the renter, not the dwelling itself. Homeowners insurance, on the other hand, covers both the dwelling and the personal property of the homeowner. The dwelling coverage in a homeowners insurance policy typically includes the structure of the home, as well as any attached structures, such as a garage or porch.
It also covers the contents of the home, such as furniture, appliances, and clothing.
Personal Property Coverage
Both renters and homeowners insurance policies provide coverage for personal property. However, the coverage limits for personal property are typically higher in homeowners insurance policies than in renters insurance policies. This is because homeowners insurance policies cover all of the personal property in the home, while renters insurance policies only cover the personal property of the renter.
Liability Coverage
Both renters and homeowners insurance policies provide liability coverage. Liability coverage protects the policyholder from financial liability if someone is injured or their property is damaged as a result of the policyholder’s negligence. The liability limits in a homeowners insurance policy are typically higher than the liability limits in a renters insurance policy.
This is because homeowners have a greater potential for liability than renters.
Cost Considerations
The cost of renters insurance and homeowners insurance varies depending on several factors, including the coverage amount, location, and the individual’s or homeowner’s risk profile. Premiums are determined by insurance companies based on actuarial data and risk assessment.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Coverage amount:Higher coverage limits result in higher premiums.
- Location:Areas with higher crime rates or natural disaster risks typically have higher insurance costs.
- Deductible:A higher deductible lowers the premium but increases the out-of-pocket expense in the event of a claim.
- Risk profile:Insurance companies consider factors such as age, claims history, and credit score when determining premiums.
Cost Comparisons
On average, renters insurance is more affordable than homeowners insurance. Renters insurance premiums typically range from $15 to $30 per month, while homeowners insurance premiums can range from $50 to $200 per month or more.
For example, a renter in a low-risk area with a coverage limit of $10,000 and a $500 deductible might pay around $15 per month for renters insurance. In contrast, a homeowner in a high-risk area with a coverage limit of $250,000 and a $1,000 deductible might pay around $150 per month for homeowners insurance.
Liability Protection
Liability coverage is a crucial aspect of both renters insurance and homeowners insurance, providing financial protection against accidents or injuries that occur on the property. Renters insurance typically includes liability coverage that protects the renter from legal claims resulting from bodily injury or property damage caused by their negligence or that of their guests.
This coverage can extend to incidents like slip-and-falls, pet bites, or accidental fires.Similarly, homeowners insurance offers liability coverage, but it is typically more comprehensive and includes protection for the homeowner, their family members, and anyone else living in the household.
This coverage not only covers accidents that occur within the home but also extends to incidents that happen on the property, such as falls from a porch or injuries sustained by a visitor in the yard. The liability limits in homeowners insurance are generally higher than those in renters insurance, providing more financial protection for the homeowner.
Additional Benefits
Beyond basic liability protection, both renters insurance and homeowners insurance may offer additional benefits, such as:
- Medical payments coverage, which helps pay for medical expenses incurred by guests or visitors who are injured on the property, regardless of fault.
- Loss of use coverage, which provides reimbursement for additional living expenses if the property becomes uninhabitable due to a covered loss.
- Pet liability coverage, which extends liability protection to the homeowner or renter for injuries or damage caused by their pets.
Additional Coverage Options
In addition to the essential coverage options, both renters and homeowners can opt for additional coverages to enhance their protection.
These optional coverages provide broader protection and peace of mind in the event of unforeseen circumstances. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider the benefits and costs associated with each coverage to determine if they align with your specific needs and financial situation.
Renters
- Renter’s Liability Coverage:Extends coverage for personal liability beyond the renter’s unit, protecting against damages or injuries caused to others outside the property.
- Replacement Cost Coverage:Provides coverage for replacing personal belongings at their current market value, regardless of their depreciated value.
- Scheduled Personal Property Coverage:Offers additional protection for valuable items such as jewelry, electronics, or artwork, ensuring they are covered for their full value.
- Loss of Use Coverage:Reimburses renters for additional living expenses incurred if the rental unit becomes uninhabitable due to a covered loss.
Homeowners
- Dwelling Replacement Cost Coverage:Guarantees coverage for rebuilding the home to its current market value, regardless of the original cost of construction.
- Extended Replacement Cost Coverage:Provides additional coverage beyond the dwelling replacement cost limit, ensuring adequate funds are available for rebuilding in case of catastrophic losses.
- Home Systems Protection Coverage:Covers repairs or replacements for essential home systems such as heating, plumbing, and electrical systems.
- Sewer and Drain Backup Coverage:Protects homeowners from the costs associated with sewer or drain backups, including cleanup and repairs.
Claims Process
Filing a claim for renters insurance or homeowners insurance involves a series of steps to ensure proper documentation and processing. Understanding the claims process can help you maximize your recovery and protect your interests.
The claims process typically begins by contacting your insurance provider and reporting the incident or loss. You will need to provide details about the incident, including the date, time, location, and cause of the loss.
Documenting the Claim
It is crucial to document the damage or loss thoroughly. Take photos or videos of the affected area and any damaged items. Keep receipts for any expenses incurred due to the incident, such as temporary housing or repairs.
Filing the Claim
Once you have gathered the necessary documentation, you can file a formal claim with your insurance company. This can be done online, over the phone, or through a claims adjuster who will visit your property to assess the damage.
Settlement
After the claim is filed, the insurance company will investigate the incident and determine the amount of coverage you are entitled to. You may be offered a settlement amount, which you can accept or negotiate if you believe it is inadequate.
Maximize Recovery
To maximize your recovery, it is essential to provide clear and accurate documentation, cooperate with the insurance adjuster, and keep track of all expenses related to the incident. If you have any questions or concerns, do not hesitate to contact your insurance provider for guidance.
Financial Implications
Understanding the financial implications of choosing renters insurance versus homeowners insurance is crucial for making an informed decision. Each option has distinct costs and potential impacts on your monthly expenses, savings, and overall financial stability.
Impact on Monthly Expenses
- Renters insurance premiums are generally lower than homeowners insurance premiums, as they cover fewer risks and liabilities.
- Homeowners insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on factors such as the value of your home, its location, and the level of coverage you choose.
- In some cases, the cost of homeowners insurance can be comparable to or even exceed your monthly mortgage payment.
Impact on Savings
- Renters insurance can help protect your belongings in case of a covered loss, potentially saving you thousands of dollars in replacement costs.
- Homeowners insurance provides coverage for both your home and its contents, which can offer significant financial protection in the event of a major disaster or loss.
- Building equity in your home can be a valuable financial asset, but it also comes with the responsibility of maintaining the property and paying for repairs or replacements.
Impact on Overall Financial Stability
- Having adequate insurance coverage can provide peace of mind and protect you from financial ruin in the event of an unexpected loss.
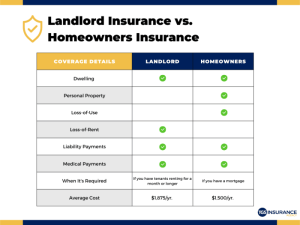
- Homeowners insurance is typically required by mortgage lenders, ensuring that your investment is protected in case of a covered event.
- Renters insurance, while not required, is highly recommended to safeguard your belongings and protect against potential liabilities.
Lifestyle Considerations
In addition to financial implications, personal lifestyle factors can also play a significant role in determining the best choice of insurance for your dwelling. These factors include mobility, stability, and homeownership goals.
Mobility
If you anticipate frequent moves or have a nomadic lifestyle, renters insurance may be a more suitable option. Homeowners insurance, on the other hand, is designed for individuals who intend to stay in their property for an extended period and are committed to maintaining it.
Stability
Homeowners insurance typically provides more comprehensive coverage than renters insurance, but it also comes with a higher premium. If you have a stable income and are confident in your ability to maintain your property, homeowners insurance may be a good investment.
However, if you are experiencing financial instability or are uncertain about your future plans, renters insurance may be a more prudent choice.
Homeownership Goals
If you plan to purchase a home in the future, homeowners insurance can help you build equity and protect your investment. However, if you are not yet ready for homeownership or are unsure about your long-term plans, renters insurance may be a more suitable option.
Legal Considerations
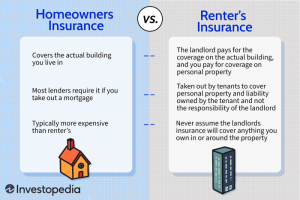
Renters and homeowners have distinct legal responsibilities regarding property protection. Renters are generally responsible for protecting their personal belongings and any alterations or additions they make to the rental unit. Homeowners, on the other hand, are responsible for the entire property, including the structure, fixtures, and any improvements they make.
Liability Protection
Both renters and homeowners need liability protection to cover potential claims for injuries or damages caused to others on their property. Renters insurance typically provides limited liability coverage, while homeowners insurance offers more comprehensive protection.
Subrogation Rights
Insurance companies often have subrogation rights, which allow them to pursue legal action against the responsible party after paying a claim. For example, if a renter’s negligence causes a fire that damages the rental unit, the renter’s insurance company may have the right to sue the renter for reimbursement.
Disclosure Requirements
When renting or purchasing a property, individuals may be required to disclose certain information about their insurance coverage. Renters may need to provide proof of insurance to their landlord, while homeowners may need to disclose their coverage to mortgage lenders.
Landlord’s Responsibilities
Landlords have a legal obligation to maintain the habitability of the rental unit, including providing essential services like heat, water, and electricity. They may also be responsible for repairing any damage to the unit that is not caused by the tenant’s negligence.
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the practical implications of choosing between renters insurance and homeowners insurance.
Let’s explore two case studies that illustrate the benefits and drawbacks of each option.
Case Study 1: Renter
Sarah, a renter, opted for a comprehensive renters insurance policy. When a fire broke out in her apartment, destroying her belongings, the insurance covered the replacement costs, including furniture, electronics, and clothing.
Without renters insurance, Sarah would have been financially responsible for replacing her lost possessions, which would have been a significant financial burden.
Case Study 2: Homeowner
John, a homeowner, had homeowners insurance with liability coverage. When a guest slipped and fell on his property, injuring themselves, the insurance covered the medical expenses and legal fees associated with the incident.
Had John not had homeowners insurance, he could have been personally liable for the damages, potentially leading to financial hardship.
Closure
The choice between renters insurance and homeowners insurance hinges on a myriad of factors, including your financial standing, lifestyle preferences, and property ownership aspirations. By thoroughly evaluating the coverage options, cost implications, and legal considerations Artikeld in this guide, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your unique circumstances.
Remember, the right insurance policy not only protects your dwelling but also provides peace of mind, allowing you to rest assured that your investment is shielded against unexpected setbacks.